As enterprises continue to re-imagine their business processes, the marketers are moving on from a ready, fire, and aim approach to deep personalization that helps brands in serving experiences with razor-sharp precision. Hyper-personalization is a technique that leverages personalized marketing techniques with artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), internet of things (IoT)-enabled devices, and real-time data.
Today’s tech-savvy consumers demand experiences in order to remain loyal to a brand. As the digital economy skyrockets, the companies are leveraging their digital environments to make ends meet. Adobe Summit 2020, the first on-demand virtual event, emphasized the necessity of new tools to engage the customers and move from exposure era to experience era.
Hyper-personalization customizes marketing communication for each individual as it predicts customer behavior, cuts through the overcrowded email inboxes and omnipresent web advertisements, and delivers the messages tailored to their needs. Such deep personalization provides lower customer acquisition costs, higher conversions, and improved customer retention. For a brand, hyper-personalization acts as a solution to get a better understanding of customer preferences and underlying motivations to create timely, relevant, and individualized messages in order to increase engagement and drive loyalty.
Gartner has predicted that AI identification of emotions is expected to influence more than half of the online advertisements in the near future. Hyper-personalization is going real-time based on emotions. Emotion detecting and recognition technology will grow to a $24 billion market in 2020.
Making the technological leap
While personalization caters to the individual, hyper-personalization utilizes behavior and real-time data to have a continuous understanding of the customers to meet their needs and expectations.
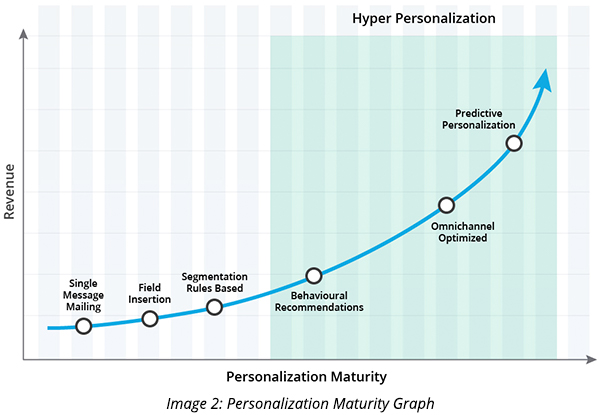
Some of the biggest online retail brands that have achieved a growth trajectory through hyper-personalization have one thing in common—they’re determined to transform from e-commerce to me-commerce. Amazon can be considered as the king of ‘Me-Commerce’ as it runs on an email recommendation engine algorithm, called ‘item-to-item collaborative filtering,' which suggests products based on 4 data points—purchase history, shopping cart items, items that you have rated or liked, and items liked and purchased by other customers. The system gets 60% higher conversions from Amazon’s on-site recommendations as compared to other brands.
Another biggest brand that has swiftly moved on to a stage of predictive personalization, where AI and ML power their recommendation engine, is Starbucks. Starbucks has raised its game by using AI and real-time data to send over 400,000 variants of hyper-personalized messages. These messages contain offers that are unique to the user’s app activity and past purchases. Their Rewards Loyalty program boasts a staggering 16 million active users.
Staying ahead of the curve with these hyper-personalization techniques:
Invest in data privacy: There’s a thin line that divides hyper-personalization and data privacy breaches, and brands must find the delicate balance to keep hyper-personalization from turning cool to creepy for the users. While it’s crucial for businesses to provide users control over their end-to-end personal data through the experience cycle, it’s also important to be transparent while using any customer data. Offering an easy opt-out option is the best practice to assure the users that the information they’ve shared is in safe hands. Organizations need to be fastidiously transparent about how they collect, process, and store data, implementing technologies that have security as a core development philosophy.
Laws like General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) have required brands to re-think strategies to deal with web application security breaches and use the valuable seed data to prove customer value over time with AI and ML.
Leverage a comprehensive identity strategy: To make your customers so happy that they describe your services as effortless, it’s essential to know your customers’ unique interests and preferences. Identity strategy allows the brands to get the information in exchange for services. AI makes the strategy more viable by doing the magic of putting you in your customers’ shoes to better understand their needs and best serve them.
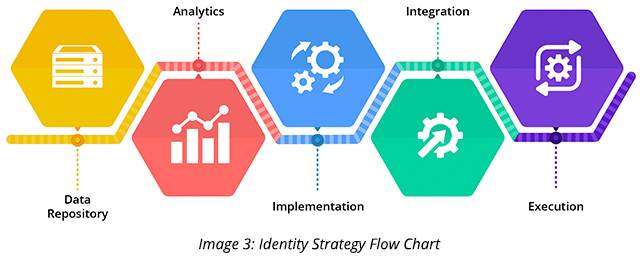
Hyper-personalization occurs when an informing technology with identity creates an environment to engage in tailor-made interactions with each person. This is where an individual-level private identity graph steps in. The graph contains individual data from trusted sources and is accessible in real-time to all components of the marketing technology stack. Here is a progression of how different components of marketing technology stack function:
- Data Repository: Includes identity graphs and identifies person-level interactions.
- Analytics: Leverages identity and customer interactions for improved personalized interactions.
- Implementation: Heavily uses identity to improve personalized interactions across various channels, such as campaign management, journey management, etc.
- Integration: Collects and distributes intelligence across integration services using the identity.
- Execution: Uses identity to activate campaign channels and digital media.
Reshape customer journey experiences: Companies have enabled product discovery powered by augmented reality (AR) to take hyper-relevance up a notch. For example, Netflix successfully combines behavioral attributes with predictive learning to send customized recommendations, which begins right from the homepage. It adds customer journey analytics in a customer data platform (CDP) to identify both known and unknown customers, making it an excellent tool for reaching out to the audience.
Hyper-personalization allows the user to scan a room, browse a product catalog, select the item, and position it at a place they want it to be placed on their cell phones. It not only improves the product discovery experience but also helps companies with data-driven personalization to enhance their product recommendation system and brand affinity.
Design a smart purchase-funnel strategy: Traditionally, the customer lifecycle was a linear journey—invest in the most popular channel to create awareness, generate interest, create desire, and perform the desired action. A modern online buyer’s journey is far from predictable, given a wide array of channels and mediums. This has led to the urgency of re-evaluating customers’ journeys and learning about their persona for deep personalization to engage the customer in the loyalty loop.
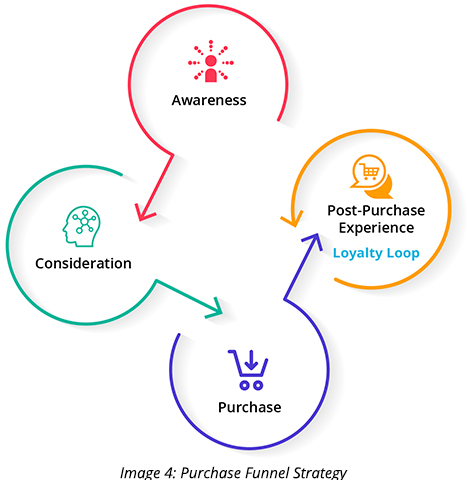
Here’s a use case to better understand the customer journey.
- Awareness – Ted’s air conditioner (AC) stops working. He reads a blog on an HVAC company’s website and wonders how old is his AC.
- Consideration – He Googles about the cost of AC replacement and realizes that it’s worth the splurge. He Googles various company reviews. He narrows down his choices, visits a few company websites, and consults a friend who recently got his AC replaced. The next day, he sees an HVAC company ad that he remembers his friend recommended.
- Purchase – He clicks on the ad, engages with the chatbot, and books a consultation.
- Loyalty Loop – After the AC is replaced, Ted praises the company’s services by giving them a good rating, good reviews on social media, and allowing the company to reach him through emails. He refers to their company every time someone complains about their AC in the locality.
The process enables higher engagement across the entire account lifecycle from the top funnel to opportunity development, closure, and post-sale. This deep personalization would give every single customer the hyper-personalized engagement they want—even before they want it.
Invest in an AI bot: While chatbots today offer basic personalization, such as demographic prediction and database parameterization (like name, location, etc.), hyper-personalization entails a fundamental shift in thinking. AI bots are expected to act like the customers’ personal assistants, not the company’s. An AI bot is built on a cognitive architecture that has a deep understanding of contextual communications by a customer as it learns by itself, reasons, interacts, and holds meaningful ongoing conversations in real-time.
The automated tool gives a virtual impression of talking to a real person on the other end. It interactively learns individual preferences, remembers, and utilizes implicit and explicit information from prior conversations. Such deep personalization is rewarded with customer loyalty and increased engagement.
Hyper-personalization allows brands to modify their strategies, manage engagement, and improve brand affinity and attention by reaching customers across different channels and devices to provide a fully-connected, seamless, and cross-device user experience. In Amazon’s CEO, Jeff Bezos’ words, “We see our customers as invited guests to a party, and we are the hosts. It’s our job every day to make every important aspect of the customer experience a little bit better.”



