Database monitoring is different from infrastructure and application monitoring. It involves monitoring database performance, slow running queries, uptime, etc. It is essential because if a database goes down, it may bring the whole application to a standstill.
Application deployment strategies in a Kubernetes Environment
Various tools help in monitoring database, like Grafana, Kibana, netstat, etc. While Kibana only collects log metrics data, netstat is apt to displace connections and routing tables. Grafana labs give more performance visibility in comparison to others. It is an open-source metric analytics and visualization tool that enables developers to write plugins from scratch to integrate with several data sources.
Even if there is a failure, we can easily troubleshoot the issue with the available stats, like database connections, number of containers running and performance, number of bytes written and read, etc. This blog throws light on how to monitor a MySQL database using Grafana and Prometheus.
Click here for a thorough comparative analysis between SQL and NoSQL databases.
Steps to Enable MySQL Database Monitoring Using Prometheus and Grafana
- Install and configure Grafana
- Install and configure Prometheus
- Install a database exporter
- Install the database
1. Install and Configure Grafana
Grafana helps in studying data, analytics, and monitoring over a period of time. It is also known as time-series analysis.
Installation steps:
Step 1: Go to Grafana’s official page and download Grafana for the respective operating system.
Execute:
wget https://dl.grafana.com/oss/release/grafana_6.5.1_amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i grafana_6.5.1_amd64.deb
Step 2: Start the server
Execute:
sudo service grafana-server start
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl start grafana-server
systemctl status grafana-server
This will start the Grafana server process with the Grafana user, which was created at the time of installation. The default HTTP port is 3000 (http://localhost:3000) and the default user and group are admin.
Default login and password of Grafana are: admin/admin
Default location Grafana will log into: /var/log/Grafana
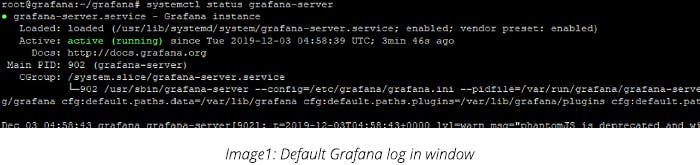
Finally, when you hit the ip_address in the browser, the homepage will be shown as below:

Enter your credentials in the login page, you will see the screen shown below:
2. Install and configure Prometheus
Step 1: Go to the official page of Prometheus and copy the link address.
Using wget command, you can install the Prometheus and untar it.
Execute:
Wget
https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/releases/download/v2.3.2/prometheus-2.3.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar -xvf prometheus-2.3.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz
mv prometheus-2.3.2.linux-amd64 prometheus-files
Step 2: Create a Prometheus user, required directories, and make the Prometheus user the owner of those directories.
Execute:
sudo useradd /bin/false prometheus
sudo mkdir /etc/prometheus
sudo mkdir /var/lib/prometheus
sudo chown prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus
sudo chown prometheus:prometheus /var/lib/prometheus
Step 3: Copy Prometheus and promtool from the Prometheus-files folder to - /usr/local/bin and, after that, change the ownership to the Prometheus user.
Execute:
sudo cp prometheus-files/prometheus /usr/local/bin/
sudo cp prometheus-files/promtool /usr/local/bin/
sudo chown prometheus:prometheus /usr/local/bin/prometheus
sudo chown prometheus:prometheus /usr/local/bin/promtool
Step 4: Move the consoles and console library directories from Prometheus-files to /etc/Prometheus folder and change the ownership to the Prometheus user.
Execute:
sudo cp -r prometheus-files/consoles /etc/prometheus
sudo cp -r prometheus-files/console_libraries /etc/prometheus
sudo chown -R prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus/consoles
sudo chown -R prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus/console_libraries
Step 5: Create the Prometheus.yml file
Execute:
vi /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
Note: All Prometheus configurations should be present in /etc/Prometheus/Prometheus.yml file.
Step 6: Copy the following content into Prometheus.yml:
global
scrape_interval: 10s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'prometheus'
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
- targets: [<mention ip_address>:9090']
- follow the intendations in yml file, otherwise it raises an error.
Step 7: Change the ownership file to the Prometheus user
Execute:
sudo chown prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
Step 8: Create a service file in this location - /etc/systmed/system
Execute:
sudo vi /etc/systmed/system/Prometheus.service
Step 9: Copy the following content to the file:
[Unit]
Description=Prometheus
Wants=network-online.target
After=network-online.target
[Service]
User=prometheus
Group=prometheus
Type=simple
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/prometheus \
--config.file /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml \
--storage.tsdb.path /var/lib/prometheus/ \
--web.console.templates=/etc/prometheus/consoles \
--web.console.libraries=/etc/prometheus/console_libraries
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Step 10: Reload the systemd service and start the Prometheus service
Execute:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl start Prometheus
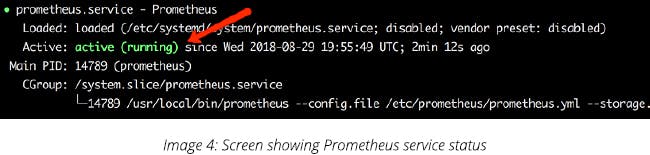
To check the Prometheus status, run the command mentioned below
Execute:
sudo systemctl status Prometheus
The output should be shown as below:
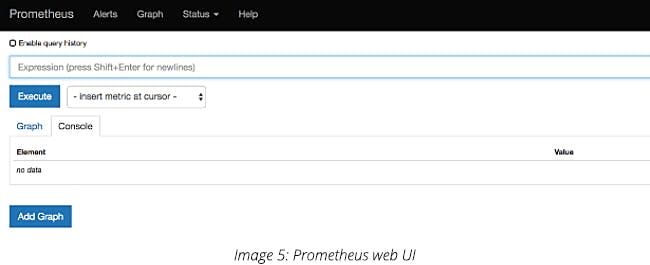
To Access the Prometheus web UI, use the default port 9090.
http://< prometheus-ip >:9090/graph
3. Installing MySQL
Step 1: Install the latest version of MySQL
Execute:
wget https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql57-community-release-el7-9.noarch.rpm
sudo rpm -ivh mysql57-community-release-el7-9.noarch.rpm
sudo yum install mysql-server
Step 2: Start the daemon and enable it
Execute:
sudo systemctl start mysqld
sudo systemctl status mysqld
Step 3: While installing it for the first time, we need to set a new password
Execute:
sudo grep 'temporary password' /var/log/mysqld.log
Output: 2019-12-11T09:28:50.095207Z 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: pdpxle;Nt9*c
The last 12 digits make a password. After executing the command below, you will be prompted to set a new password. The password should be a combination of alphabets in lowercase, upper case, numbers, and a special character.
Execute:
sudo mysql_secure_installation
Output: If the existing password for the user account root has expired. Please set a new password.
New password:
The Estimated length of the password: 100
Change the password for root? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) :
Press 'yes' all the times as many times as prompted. It is for security and old data clean-up.
For Testing Mysql connection run the below command:
mysqladmin -u root -p version
When prompted, enter the new password to log in.
4. Installing the Mysqld exporter
Step 1: Download the latest version of mysqld_exporter
Execute:
mkdir mysqld-exporter
cd mysqld-exporter
wget https://github.com/prometheus/mysqld_exporter/releases/download/v0.11.0/mysqld_exporter-0.11.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz
Step 2: Extract the downloaded archive in your current folder
Execute:
tar xvzf mysqld_exporter-0.11.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz
Step 3: Create a user for Prometheus
Execute:
cd mysqld_exporter-0.11.0.linux-amd64/
sudo mv mysqld_exporter /usr/local/bin/
sudo useradd -rs /bin/false prometheus
sudo vi /lib/systemd/system/mysql_exporter.service
[Unit]
Description=MySQL Exporter
User=prometheus
[Service]
Type=simple
Restart=always
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/mysqld_exporter \
--config.my-cnf /etc/.exporter.cnf \
--collect.auto_increment.columns \
--collect.binlog_size \
--collect.engine_innodb_status \
--collect.engine_tokudb_status \
--collect.global_status \
--web.listen-address=0.0.0.0:9104
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl status mysql_exporter
Output:
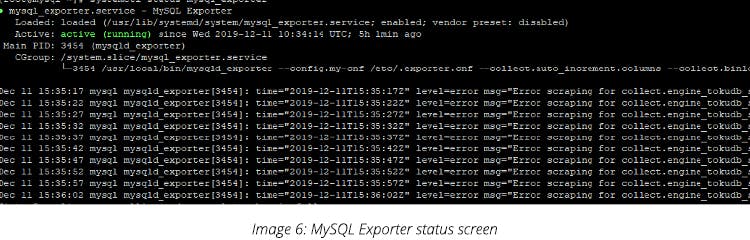
Default port is 9104 metrics for mysqld_exporter(http://< ip_address >:9104)

Add it to Prometheus target.
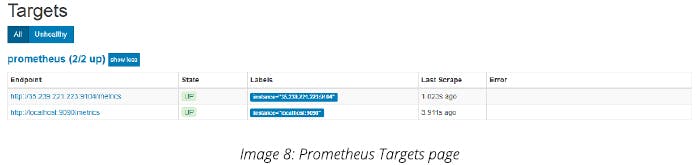
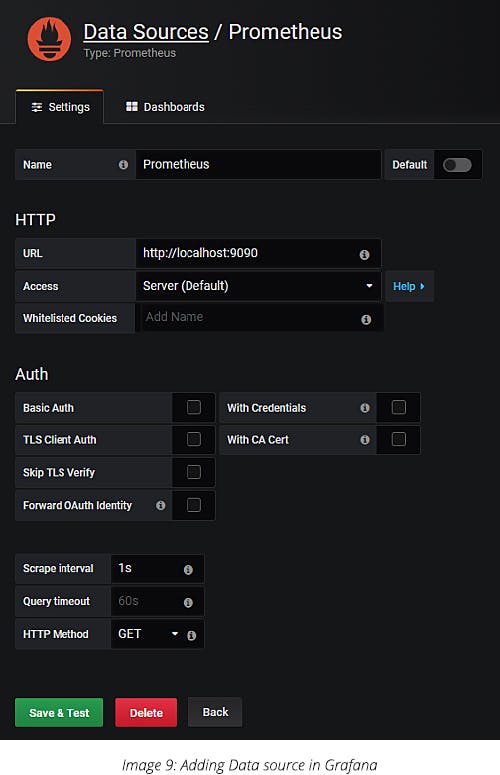
Step 4: Set Prometheus as Grafana data source. Add the data source and name it Prometheus. Enter the URL and click on Save & Test.
Step 5: Download the dashboards for Grafana
Execute:
Cd /etc/Grafana
Sudo mkdir dashboards
Cd dashboards
Sudo wget https://github.com/percona/grafanadashboards/blob/master/dashboards/MySQL_Overview.json
Step 6: Import the MySql dashboard into Grafana
Go to Grafana dashboard. Run this Url in browser: http://< ip_address >:3000
On the left menu, click on the plus icon and click on import. Then, click on ‘Upload JSON file’ and go to the directory where the JSON file has been downloaded. Choose it to complete the upload.
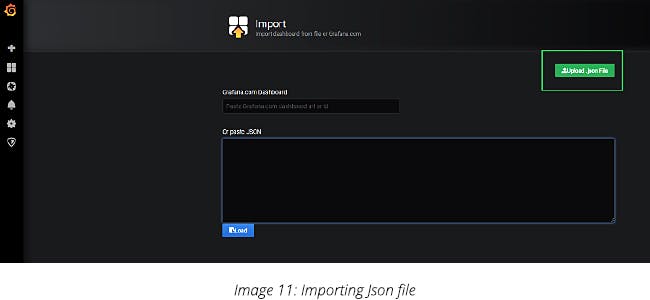
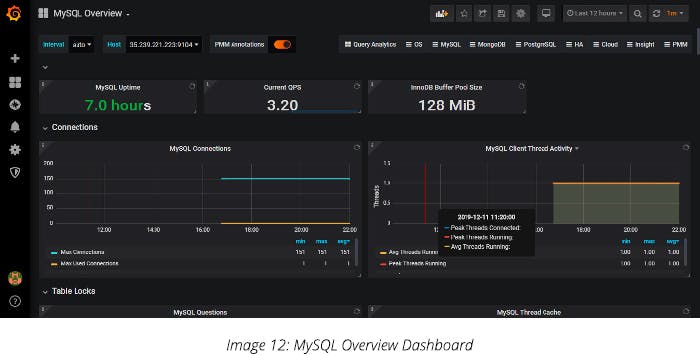
Finally, your dashboard will be imported with real-time updates of MySQL.
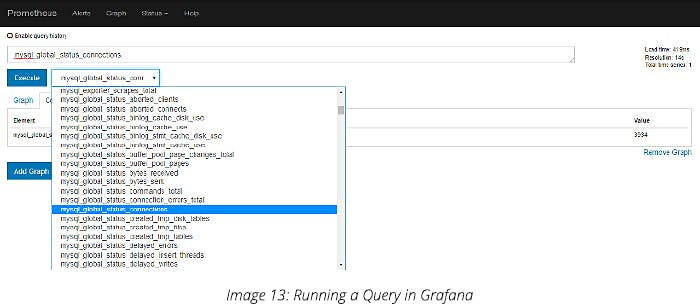
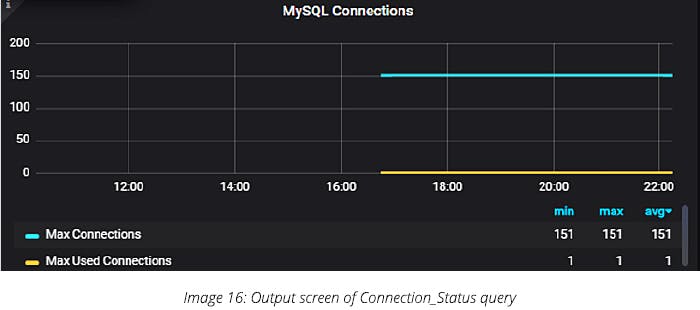
If you want to run a particular query: Go to Prometheus > click on Graph > click on insert metric: select the query in the drop-down menu that you want to execute > click on the execute button.
For example, to run a query to know how many connections are there, we run a query as shown below:
Output:
It will display how many users are there currently in MySQL

If you want a graph, click on the graph button, which will get executed as below:
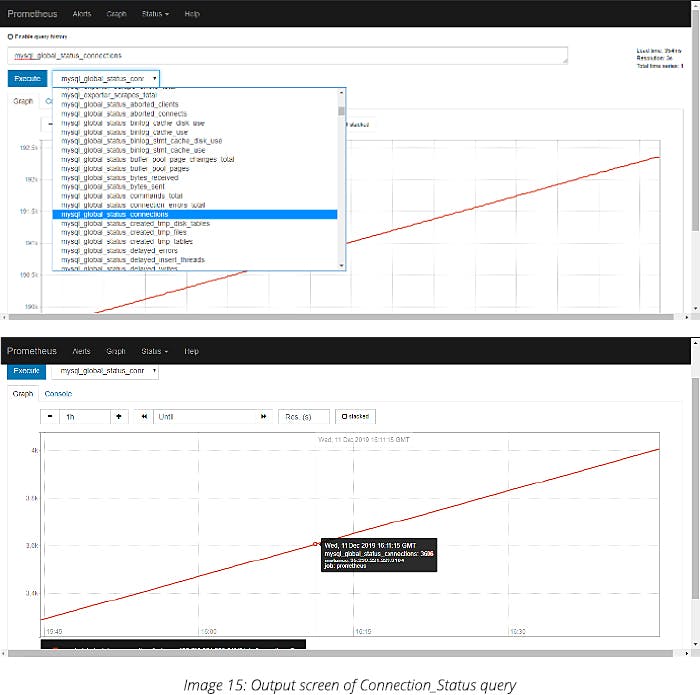
In Grafana, you will see the output as shown below:
There are many database monitoring tools available for data visualization, but Grafana labs give more performance visibility compared to others. Grafana and Prometheus help us monitor not only database servers but also the applications that are running on virtual machines as well as containers.



