Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipeline is a fantastic way to make your app development process efficient. It reduces risks, improves build quality, speeds-up build releases, decreases manual efforts, and even makes rollbacks easier.
The pipeline contains varied sets of tools and frameworks to support development, QA, and operations teams in delivering the desired apps at a fraction of the cost and time to the end users.
An Overview of Key Technologies
In order to create effective pipeline-enabled automation, several key technologies need to be put into place. Here is a brief overview of technologies we have seen work wonders for our clients.
- Jenkins
Jenkins is at the heart of an automated build solution. It’s an open-source platform with hundreds of plugins that continuously monitor the build state of applications. - Version Control
Jenkins is unaware of any changes in your application codebase until your version control system sends a notification of a change via a ‘hook’. Examples of version control systems that feature ‘hooks’ include Git and Bitbucket. - Sauce Labs
Sauce Labs is a cloud platform explicitly designed to run cross-platform automated test suites.
Why Should You Implement a CI/CD Pipeline for Your App?
Implementing an automated build pipeline is not a trivial process. However, many positive benefits accrue once you implement this automation, giving you a substantial ROI.
The most significant reason for implementing the CI/CD-enabled pipeline is the staggering amount of time you will save on the build process. In our experience, the time to complete the build process dropped from two (or more) days to just a few hours!
Another key benefit derived from our solution is a vast reduction in procurement costs. No matter how many new devices you add to the device support policy, Sauce Labs can handle it.
The automated build system we discuss here allows you to define an environment dynamically. This means you don’t have to worry about creating a duplicate build for each environment.
Pipeline Creation for Mobile Applications
Let's take a look at some details on pipeline creation. We start with the iOS environment and follow that with Android.
1. iOS CI/CD Pipeline
The iOS build process shares similarities to that used for Android. However, due to Apple’s unique requirements, there are substantial differences. Image 2 shows the iOS CI/CD pipeline process.
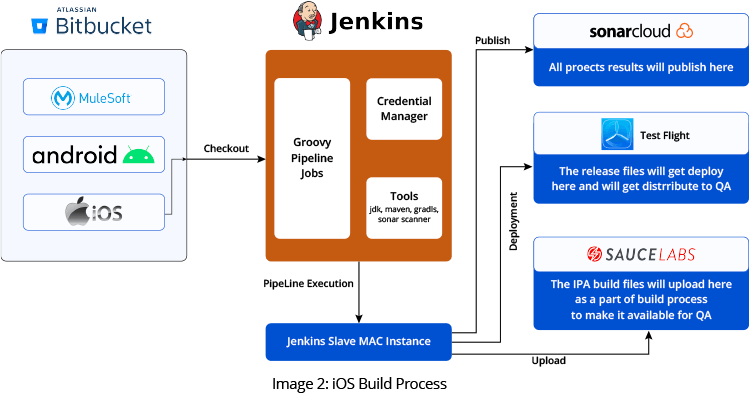
- First, we check out the source code from the Bitbucket repository. The secret keys and API keys get downloaded from a different repository and flow into the source code using the environment.
- For the second step, Apple requires the MAC OS platform to perform the second step. For this purpose, we use MAC Stadium cloud services. After attaching the virtual MAC machine as a secondary to Jenkins, the entire Apple iOS build takes place in the cloud.
- At this point, unit testing occurs and the results are published on a Jenkins job page.
- Next, we perform a code “smell test”, using Sonar Cloud to check code structure, integrity, and security.
- Once the Sonar Cloud validation is complete, the build file is digitally signed with a certificate.
- The iOS build file is deployed to TestFlight and distributed.
- The build file is assigned a unique identifier and is uploaded to Sauce Labs. We trigger the QA test in the final stage according to job-specific parameters.
2. Android CI/CD Pipeline
There are multiple steps required to fulfill the build process requirements. The steps are illustrated in Image 3.
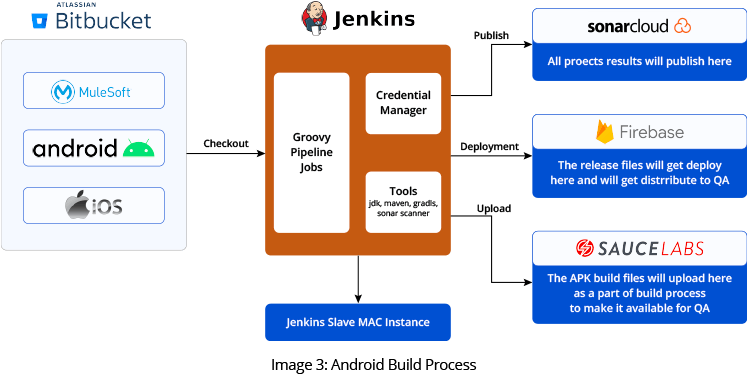
- First, we check out the source code from the Bitbucket repository. The secret keys and API keys get downloaded from a different repository and flow into the source code using the environment.
- In the second step, we create the build file. Here we have multiple environments that are selected using Jenkins parameters.
- At this point, unit testing occurs and the results are published on a Jenkins job page.
- Next, we perform a code “smell test”, using Sonar Cloud to check code structure, integrity, and security.
- Once the Sonar Cloud validation is complete, the build file is digitally signed with a certificate.
- The deployment process follows, and we upload the signed build file to Firebase and distribute it to QA.
- The build file is assigned a unique identifier and is uploaded to Sauce Lab. We trigger the QA test in the final stage according to job-specific parameters.
Sauce Labs Integration with CI/CD Pipeline
We integrate Sauce Labs with the CI/CD pipeline using the steps below.
STEP 1
- Install ‘Sauce OnDemand Plugin’ in the Jenkins Plugin manager
- Register/Login to the Sauce Labs account and create an access key for your username. You can find it under ‘User Settings’ after logging in.
- Add the Sauce Labs credentials under Jenkins Manage credentials.
- Use the Sauce Support option in the Jenkins job option to select the added Sauce Labs credential in the Jenkins Manage Credentials dialog.
NOTE: Sauce Labs has datacenters in multiple regions globally. When adding credentials, you must select the region based on where you have licensed your mobile devices.
The previous step ensures that a secure session is established and helps Jenkins interact with Sauce Labs.
STEP 2
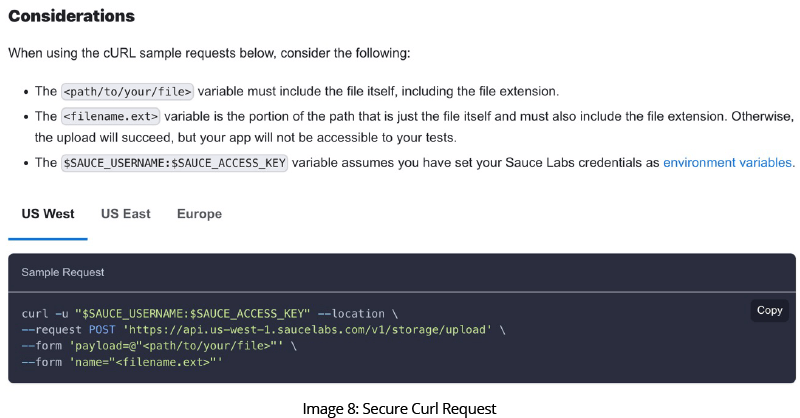
Use the curl command with security options to upload the appropriate files to Sauce Labs as recommended by Sauce Support.
As per the mobile devices license in Sauce labs, add the device names in the choice parameters of Jenkins jobs.
Build environments are controlled at the Jenkins level. All keys and configuration are maintained in a separate secured Bitbucket repository. The environment selection of the Jenkins job ensures that the appropriate configuration files and keys are inserted into the codebase from this separate repository using the Jenkins “Active Choice Parameter” plugin.
STEP 3
The automation suites are based on the Maven build tool and can be triggered via Maven build commands. Here is an example:
# mvn clean install
You determine the selection of the mobile devices using the parameters mentioned in Step 2. The build file will be named after the environment, date, and build number. The selection of a build file is dynamic based on the Jenkins job.
STEP 4
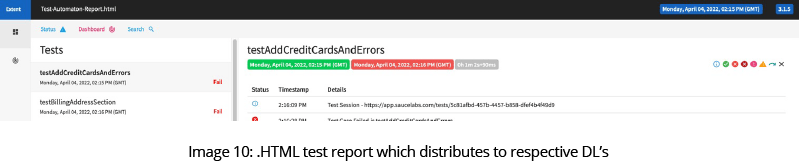
Once the “Sauce OnDemand” plugin is installed in Jenkins, it records the logs of test suites in Sauce labs. Use the HTML publisher plugin in Jenkins, post them in the Jenkins job at each build level.

STEP 5
The same HTML file will be sent to respective DLs via email as an attachment from Jenkins using the Email Extension Plugin.
Key Obfuscation
An essential part of CI/CD pipeline automation is the ability to obscure sensitive access keys and other credentials. Upload the API keys and property files to a separate secured repository. This technique works best if you create a set of branches representing each of the environments you plan to use (e.g., testing, staging, production).
We use a Jenkins pipeline to perform key obfuscation via the Active Choice Reactive Parameter plugin. The syntax is shown in Image 11:
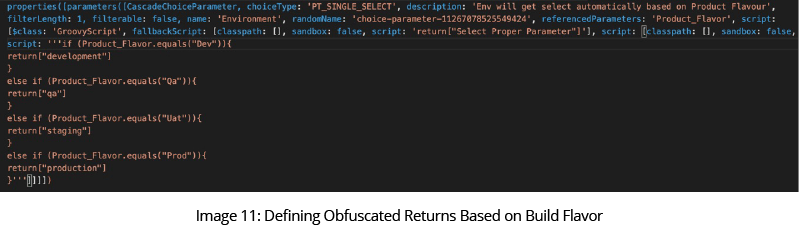
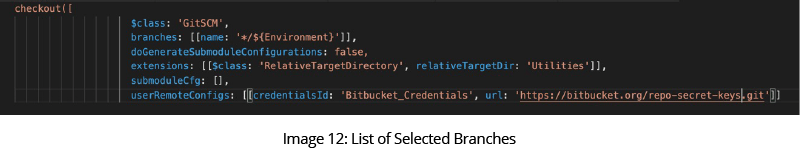
Image 12 shows the branches that are automatically selected based on the above choices.
Single Build Dynamic Environment Selection
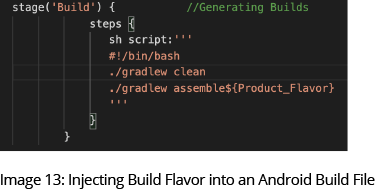
The ability to dynamically select the environment saves you from having to create duplicate builds. Instead, you can enable dynamic environment selection by executing the build file and build flavors representing respective environment values.
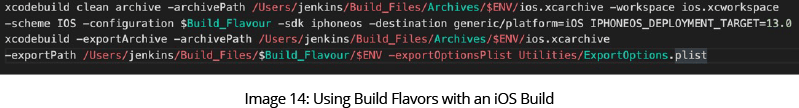
The build flavors are embedded in the code by developers. During the build process, we inject the environment tag into the build command definition so it will generate the desired build.
ANDROID
iOS
Conclusion
The process of certifying a mobile app that you develop is tedious and time-consuming. Without the proper automation tools, the pace at which you deploy new releases slows to a crawl. The result is that app consumers become frustrated, and you lose business.
In this blog, we showcased how three key technology components, version control, a CI/CD pipeline, and Sauce Labs, are employed to automate the build certification process.




