The recent time saw a lot of buzz around Blockchain and Bitcoin (a type of Cryptocurrency) as more businesses planned to adopt them and many countries plan to create their own digital currencies. It has also been speculated that the Indian digital currency would be named Lakshmi (Goddess of wealth). Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the central Indian governing bank, has created a task force to assess the possible granting of legal tender status to Bitcoin and other digital currencies, although the regulations in the digital currency remains a challenging task.
Bitcoin came into existence in the year 2009. It was invented by an unknown person or a group of people under the name Satoshi Nakamoto and released as open-source software in 2009. The first transaction took place on Jan 3rd, 2009. Bitcoin is only one application of Blockchain.
Why do we need a digital currency?
Well, we all have sent a mail to someone or a picture, pdf, word doc, etc. Why can’t money can be sent in the same way? Peer-to-peer communication without requiring any third-party involvement to validate the entire process, how good and simple the process would be. If a document can be sent that way, then why not money?
The problem which comes here is called Double spending.
Double spending means that you are creating as many copies of the original document as you are sending them. The original version is never transferred from your system and each recipient gets a copy of what you had. So, it results in multiple copies/duplicity of the original document and this thing cannot be applied with money, simply because multiple copies of currency cannot be valid. Therefore, for this reason, you need to have a bank, credit card, wallet or any third-party clearance which can validate money transfer from one party to another.
Can there be a way for direct transfer of money?
Having accurate information and knowledge source of data when dealing with transactions of value is of utmost importance. There are many fraudsters/hackers who can easily dupe you.
Direct money transfer can be achieved with a technology called blockchain which can provide a sole source of truth which is verifiable, tamper-proof, and cannot be changed.
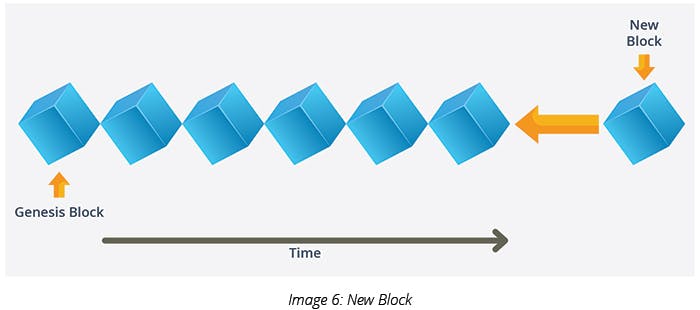
Blockchain is a constantly growing ledger that keeps tracks of all the transactions which have taken place in a secure, chronological, and immutable way. The ledger cannot be changed later. Once a transaction has been added to it, it cannot be removed from it and all the blocks are connected right up to the first block also known as the Genesis block.
All the blocks are secured cryptographically by a SHA256 (Secure Hash Algorithm) developed by NSA which generates a hash of the content/data. It is a one-way process and generates a unique fingerprint. The difficulty level increases every two weeks with more computing power getting added to the network. To solve a block, there must be a certain number of leading zero’s in a hash (which also keeps on changing). The process to generate such a hash is by entering a unique value of nonce (number used once)
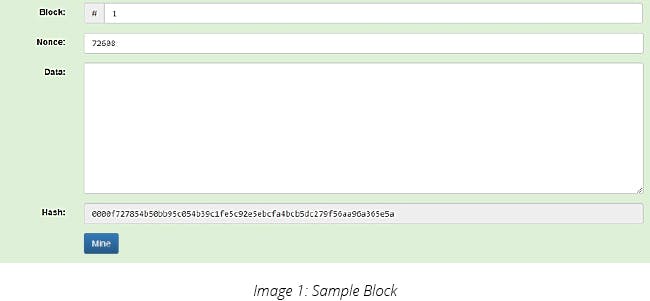
1) Below is an example of a block, which has a certain no. of leading zero’s which constitutes a valid hash (starting with a certain number of zeros).
2) Now, If I change the value of the text (data), Hash is changed and the block becomes invalid.
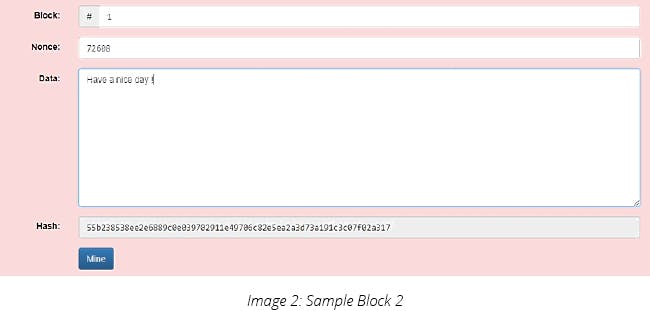
Here, the block is broken and I need to generate a new Nonce (number used once) to make the block valid again.
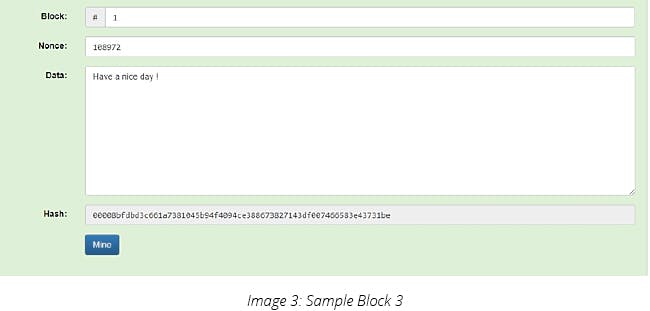
3) Either, you can randomly enter nonce, or use powerful computing to calculate valid Nonce.
4) Taking this concept further, what happens in Blockchain is that all the blocks are attached to each other with the hash of the previous block right up to the first block (Genesis block) to constitute a long chain of blocks.
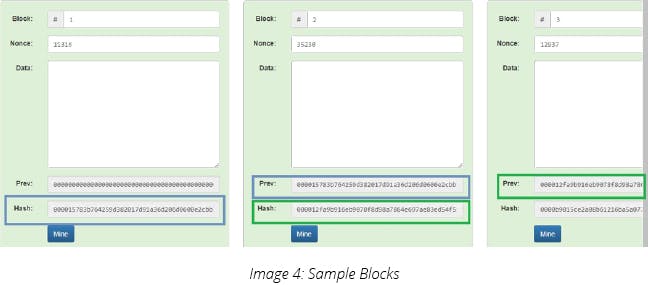
5) If I change the value in any of the blocks, all the further blocks become invalid and I will have to regenerate the nonce for all the blocks. With even the most powerful computing available it is almost impossible for a hacker to generate all the nonce without being detected as a fresh block is getting added roughly after every 10 mins in the Blockchain.
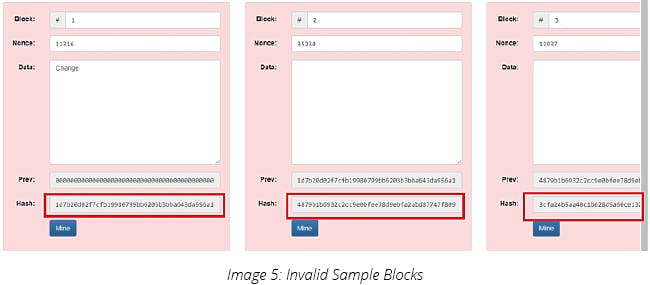
Here, all the hash gets broken once the data is changed after a block has been added in a blockchain.
Blockchain in action
Forking -
In normal software terminology, forking means creating a separate branch from the main branch of development. In blockchain terminology, it occurs when a blockchain diverges into two separate paths either with regard to a network’s transaction history or a new rule in deciding what makes a transaction valid.
Why do forks happen?
Forks on bitcoin happen on a regular basis, whenever two or more miners solve a block at the same time, for a while, there are extra chains. Eventually one of the chains wins over the others and everyone follows that chain it creates an orphan block.
Types of Forks -
Hard fork: Introduces a change that everyone will have to incorporate. Happened on 1st Aug 2017, which was a user-activated hard fork, it caused a split in the chain. It happened at Block # 478,558 when a block size exceeding 1 MB was pushed on the network and it resulted in a different digital currency known as Bitcoin Cash.
Soft fork: backward compatible, not required to upgrade. Official activation on 24th Aug 2017 at Block# 4,81,824.
To get more information on Cryptocurrencies, download this white paper.



